Code:
const Vec3 TOWER_SHIFT( 0, 0, 200 );
const Vec3 FLOOR_SHIFT( 0, 200, 0 );
Vec3 tower = TOWER_SHIFT * (-4.5);
Vec3 floor( 0 );
Mesh a, b, mesh;
Builder builder;
SculptRoom room;
void main() {
room.clear().toSurface();
// capsule
{
a = builder.capsule()
.startPosition( Vec3( 0 ) )
.endPosition( Vec3( 40, 50, 60 ) )
.startRadius( 30 )
.endRadius( 50 )
.details( 0.1 )
.build();
b = builder.capsule()
.startPosition( Vec3( 0 ) )
.endPosition( Vec3( 20, 30, 40 ) )
.startRadius( 20 )
.endRadius( 30 )
.position( Vec3( 20, 30, 40 ) )
.details( 0.5 )
.build();
draw();
}
// cone
{
a = builder.cone()
.radius( 50 )
.height( 120 )
.details( 0.1 )
.build();
b = builder.cone()
.radius( 40 )
.height( 80 )
.position( Vec3( 10, 20, 30 ) )
.details( 0.5 )
.build();
draw();
}
// cuboid
{
a = builder.cuboid()
.side( Vec3( 100, 80, 60 ) )
.details( 0.1 )
.build();
b = builder.cuboid()
.side( Vec3( 30, 50, 70 ) )
.position( Vec3( 20, 30, 40 ) )
.details( 0.5 )
.build();
draw();
}
// cylinder
{
a = builder.cylinder()
.positionTop( Vec3( 80, 0, 0 ) )
.positionBottom( Vec3( 0, 0, 0 ) )
.radiusTop( 40 )
.radiusBottom( 50 )
.details( 0.1 )
.build();
b = builder.cylinder()
.positionTop( Vec3( 70, 0, 10 ) )
.positionBottom( Vec3( 0, 0, 0 ) )
.radiusTop( 20 )
.radiusBottom( 30 )
.position( Vec3( 20, 30, 40 ) )
.details( 0.5 )
.build();
draw();
}
// ellipsoid
{
a = builder.ellipsoid()
.radius( Vec3( 80, 60, 40 ) )
.details( 0.1 )
.build();
b = builder.ellipsoid()
.radius( Vec3( 20, 40, 60 ) )
.position( Vec3( 20, 30, 40 ) )
.details( 0.5 )
.build();
draw();
}
// gear
{
a = builder.gear()
.startPoint( Vec3( 0, 0, 0 ) )
.endPoint( Vec3( 90, 90, 90 ) )
.topRadius( 30 )
.bottomRadius( 50 )
.relativeHoleRadius( 0.3 )
.depth( 0.5 )
.sharpness( 0.2 )
.teeth( 3 )
.details( 0.1 )
.build();
b = builder.gear()
.startPoint( Vec3( 20, 20, 20 ) )
.endPoint( Vec3( 50, 50, 50 ) )
.topRadius( 50 )
.bottomRadius( 50 )
.relativeHoleRadius( 0.3 )
.depth( 0.2 )
.sharpness( 1.0 )
.teeth( 6 )
.details( 0.5 )
.build();
draw();
}
// ngon
{
a = builder.ngon()
.startPoint( Vec3( 0, 0, 0 ) )
.endPoint( Vec3( 90, 90, 90 ) )
.topRadius( 30 )
.bottomRadius( 40 )
.relativeHoleRadius( 0.3 )
.teeth( 3 )
.details( 0.1 )
.build();
b = builder.ngon()
.startPoint( Vec3( 20, 20, 20 ) )
.endPoint( Vec3( 50, 50, 50 ) )
.topRadius( 50 )
.bottomRadius( 50 )
.relativeHoleRadius( 0.2 )
.teeth( 6 )
.details( 0.5 )
.build();
draw();
}
// tube
{
a = builder.tube()
.startPoint( Vec3( 0, 0, 0 ) )
.endPoint( Vec3( 30, 50, 70 ) )
.topRadius( 30 )
.bottomRadius( 40 )
.relativeHoleRadius( 0.8 )
.topScale( 2.0 )
.bottomScale( 1.0 )
.details( 0.1 )
.build();
b = builder.tube()
.startPoint( Vec3( 10, 20, 30 ) )
.endPoint( Vec3( 20, 40, 60 ) )
.topRadius( 20 )
.bottomRadius( 20 )
.relativeHoleRadius( 0.2 )
.topScale( 1.5 )
.bottomScale( 3.0 )
.details( 0.5 )
.build();
draw();
}
// sphere
{
a = builder.sphere()
.radius( 70 )
.details( 0.1 )
.build();
b = builder.sphere()
.radius( 40 )
.position( Vec3( 30, 40, 50 ) )
.details( 0.5 )
.build();
draw();
}
}
void draw() {
floor = Vec3( 0 );
// add
mesh = a | b;
mesh.tools().transform().position( tower + floor ).run();
room += mesh;
floor += FLOOR_SHIFT;
// subtract
mesh = a - b;
mesh.tools().transform().position( tower + floor ).run();
room += mesh;
floor += FLOOR_SHIFT;
// intersect
mesh = a & b;
mesh.tools().transform().position( tower + floor ).run();
room += mesh;
tower += TOWER_SHIFT;
}
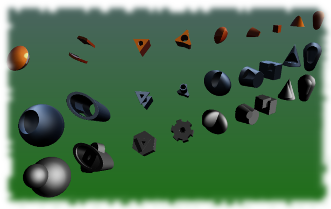
When 3D-Coat is launched, you get the following:
Pay attention to the wireframe density: it is different for each mesh and is maintained after boolean operations.
The code can be reduced, knowing that `
MeshX::build()` и `ToolsX::run()` can be functors. That means we can write: ...
a = builder.sphere()
.radius( 70 )
.details( 0.1 )
();
... ...
mesh.tools().transform().position( tower + floor )();
...
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий